Statistics from the
Nigerian Stock Exchange for March 31st, 2019 indicates that the total market capitalization
was N11.7 trillion generated from 169 companies listed on the stock within 12
sectors. Over the years, agriculture,
construction and real estate, consumer goods, industrial goods, healthcare, information
and communications technology, natural resources and, oil and gas have been seen
the significant industries contributing to the country’s economic growth and sustainability.
Activities and expected
functions of these industries are interwoven. For instance, real estate and
construction cannot make its contribution to the Gross Domestic Product without
the support industrial goods, ICT and healthcare. As businesses continue to
innovate at process and product levels, Infoprations
has discovered that a new industry is emerging. It appears that Total Real
Estate Solutions is evolving from the stable of Alpha Mead and Facilities
Management, Nigeria’s leading FM company.
After
several months of monitoring the shapes the industry is taking, Infoprations believes that TRES is about
serving most or all the needs of a particular group of customers, signifying that
companies that deem it fit to compete in the space must position themselves
using a needs-based strategies. TRES is also about segmenting customers in different
ways.
For
example, total real estate solutions should not neglect the people at the
bottom of the pyramid, people in the rural areas. There must be inclusive
solutions not only premium solutions to the people in urban areas and upper of
the pyramid. Beyond people, TRES companies should consider businesses at lower
ebb too. Companies should not position themselves using variety-based
strategies. Solutions in TRES should not be communicated using the product or
solution varieties.
Forces
Underpinning and Constraining Existing Industries
As it is now, TRES is a
combination of real estate development, security, facilities and healthcare
management industries. The idea is to have an industry that provides aggregated
solutions for the built environment and the users, appropriating integrated
processes and solutions or products. These industries are being measured quarterly
and yearly by the National Bureau of Statistics using real estate and
construction, water supply, sewerage, waste management and remediation,
administrative and support services, human health and social services,
professional, scientific and technical services.
In our model, we
considered water supply, sewerage, waste management and remediation, and administrative
and support services as part of the facility management industry. Healthcare
management was analysed within human health and social services. However, we
did not dispute the fact that the healthcare management segment of the TRES
could also be measured within the administrative and support services,
especially when an FM company is engaged to maintain health equipment not the
entire health facility. The security aspect of the TRES was analysed employing
relevant Gross Domestic Product data within professional, scientific and
technical services. Real estate and construction were analysed differently
using individual data released by the National Bureau of Statistics.
Our analysis reveals
that companies in TRES industry need to make a number of strategic moves in the
next few years, for the industry to make meaningful impacts and contribution to
the GDP. The performance of the analysed industries in the last 3 years is low
compared to international standards.
From the global
competitiveness perspective, businesses in the TRES and stakeholders need to devise
strategies and mechanisms that would help in improving efficacy of corporate boards, macroeconomic
environment, foreign competition, local competition, goods market efficiency, labour
market efficiency, financial services meeting business needs, ease of access to
loans, financial market development, availability of latest technologies, firm-level
technology absorption, local supplier quantity, local supplier quality, capacity
for innovation, spending on research and development.
This is imperative
because our analysis indicates that existing industries that TRES is leveraging
connected with these factors negatively between 2016 and 2017, signifying poor
performance at process, product or solution and technological levels. In our
analysis, we found that the higher the rankings (poor status) of these factors,
the less the contribution of the industries to the GDP growth in 2016 and 2017.
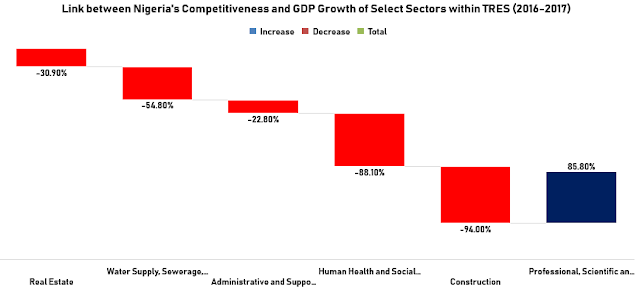
For instance, a 1 point
increase in the ranking of the factors in 2016 reduced the real estate
contribution to the GDP by 30.9%. This was dipped to 19.8% in 2017. This is an
indication that companies and governments’ efforts improved the rankings of the
factors positively in 2017. The similar
efforts were futile in 2016 and 2017 for the water supply, sewerage, waste
management and remediation. Our analysis shows that the increase in the
rankings led to 54.8% and 85.7% reduction in the contribution of the sector to
the GDP during the years.
The narrative was not
different from the administrative and support services. The sector’s
contribution was affected by 22.8% and 57% in 2016 and 2017 respectively. For
the human health and social services, the poor rankings of the factors denied
its contribution to the GDP by 88.1% in 2016 and 99% in 2017. With a 13.4%
reduction, the poor rankings only had a mild impact on the construction sector
in 2017. The impact was 94% in 2016. The 2016’s reduction attained by the
construction sector was surged by 0.8% for the professional, scientific and
technical services sector in 2017. The rankings affected the sector’s
contribution by 94.8% during the year. In 2016, 85.8% was recorded for the
sector, our analysis reveals.
Link among the GDP growth of the
select sectors
Since the real estate
is the base of the total real estate solution, we carried connection analysis
of the previous performance of the industries TRES is leveraging. From the
analysis, it is clear that real estate linked with construction and
professional, scientific and technical services positively, while negative
connection was recorded in the other three sectors. A one percent increase in
the contribution of real estate to the GDP between 2016 and 2018 led to 11.1%
increase in the contribution of the construction sector to the GDP.
Over 10% increase in
the contribution of professional, scientific and technical services was found
when real estate contribution was at 1%. For the water supply, sewerage, waste
management and remediation, a 1.6% reduction in its contribution was discovered
when real estate had 1% contribution to the GDP. It was a 92.2% reduction in administrative and
support services sector when real estate attained 1% contribution. One percent
contribution of the real estate was also discovered as 30.5% reduction in the
contribution of the human health and social services to the GDP.
From the insights, it
is obvious that TRES performance would largely depend on the extent to which
companies and stakeholders exploit opportunities in real estate, construction
and professional, scientific and technical services. As an emerging industry,
TRES is also likely to have proper shape when the weaknesses and threats in
other sectors are eliminated using appropriate strategies.
For instance, efforts
should be made to remove clogs within the market fundamentals, performance
measurement, regulatory and legal, transaction process and sustainability in
the real estate sector to make the sector highly transparent. This is necessary
based on the fact that the country’s poor ranking in the global
real estate transparency index affected the real estate sector’s
contribution to the GDP by 13.5% between 2016 and 2018.
Critical
Capabilities Transferring (CCT)
Companies with
integrated solutions in each of the industries that form TRES have a better
chance of winning in TRES space, our analysis suggests. In this regard, Alpha
Mead’s rapid turnaround, in terms of strategic business unit with vertical
integration that allows the combination of existing resources towards
sustainable value delivery, is essential to its cost reduction and effective operational
efficiency in the new space.

Comments
Post a Comment