Every
day, the world becomes complex. Social, political and economic problems that
were much easier to identify previously are now hidden and can only be
discerned in a longer perspective. Various governance templates have been
created and tweaked in the course of finding solutions to different problems
across the world.
From
the developed to developing countries, models have been adopted and still being
employed to address problems threatening human existence and ecosystems. The
end results are social, economic and political sustainability. Unfortunately,
issues like business continuity, security threats, risk management, corporate
social responsibility and financial instability have put increased pressure on
FM companies to deliver efficiencies in the workplace and other environments
where they are needed.
Like
other industries in Nigeria, sustainability has become a matter that practitioners
and captains of the FM industry must not play with it. People and businesses’
attention has been shifted to sustainable solutions from unsustainable ones in
the last three years, occasioned by the Sustainable Development Goals.
How is Sustainable FM Contextualised in Nigeria?
Infoprations
discovered that sustainable FM occurs when companies provide solutions that
ensure building and workplace sustainability.
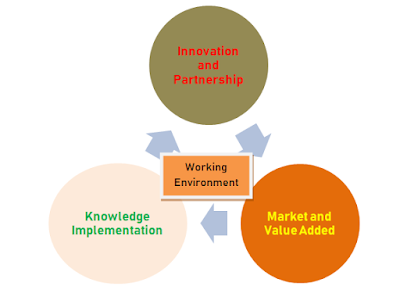
The
first strategy towards sustainable FM solutions delivery is the optimization of
processes within the working environment. FM companies must ensure that the
right processes are developed and followed while initiating and delivering
varied FM solutions. This is imperative because the fragmentation of work
processes frequently led to unsustainable working conditions and a divide
between human and nature. This strategy is the heart of sustainable FM practices.
The developed and validated processes are expected to aid development of innovative
solutions to problems affecting hard and soft facilities at home and workplace.
Beyond
creating sustainable solutions internally, FM companies equally need other
professionals in the built industry. This is a partnership, which must be
strategic at the solutions formulation and problem execution stages. Knowledge
implementation as the third stage of sustainable FM practices in Nigeria entail
appropriation of the organisation’s tacit and explicit knowledge during
solutions initiation and delivery.
Without
this, the last stage, market’s dynamic understanding and value addition would
not be attained. Within the market and value added stage, natural capital must
be valued. FM companies cannot also do without renewable resources application
because the global leaders’ focus is to ensure quality and healthy living for
every human and by extension facility by 2030.
Comments
Post a Comment